[MicroPython]TPYBoard 飞奔的装甲一号
智能小车作为现代的新发明,是以后的发展方向,他可以按照预先设定的模式在一个环境里自动的运作,不需要人为的管理,可应用于科学勘探等等的用途。智能小车能够实时显示时间、速度、里程,具有自动寻迹、寻光、避障功能,可程控行驶速度、准确定位停车,远程传输图像等功能。下面带大家做一个智能蓝牙小车,用手机APP来控制小车前进、后退、向左、向右、停止,本次蓝牙小车的设计在于探索蓝牙智能小车的设计理念及设计方法,学习一下PWM控制电机差速来控制小车的方向,下面就动手搞起来吧!!!!!
1.效果展示
给大家上视频连接,可以蓝牙控制,可以手柄控制哦
https://v.qq.com/x/page/k0721or47dw.html
2.材料准备
TPYBoard v102 1块
蓝牙串口模块 1个
TPYBoard v102小车扩展板(包含4个车轮,4个电机)
18650电池 2节
数据线 1条
杜邦线 若干
蓝牙APP (http://old.tpyboard.com/download/tool/190.html)
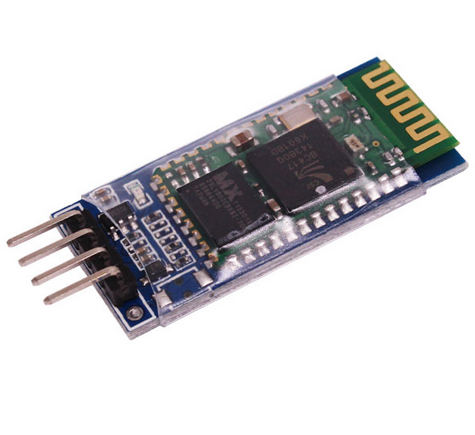
3.蓝牙模块
蓝牙( Bluetooth):是一种无线技术标准,可实现固定设备、移动设备和楼宇个人域网之间的短距离数据交换(使用2.4-2.485GHz的ISM波段的UHF无线电波)。
我们在此使用的蓝牙模块(HC-06)已经在内部实现了蓝牙协议,不用我们再去自己开发调试协议。这类模块一般都是借助于串口协议通信,因此我们只需借助串口将我们需要发送的数据发送给蓝牙模块,蓝牙模块会自动将数据通过蓝牙协议发送给配对好的蓝牙设备。

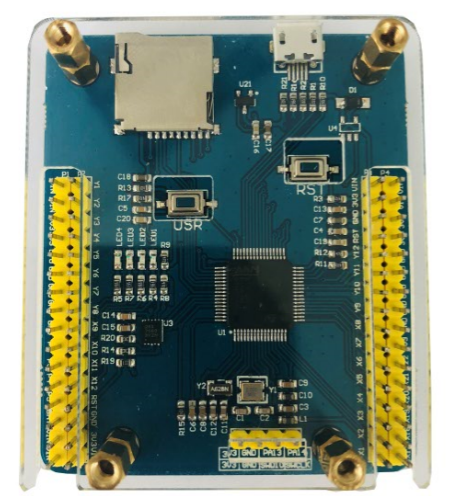
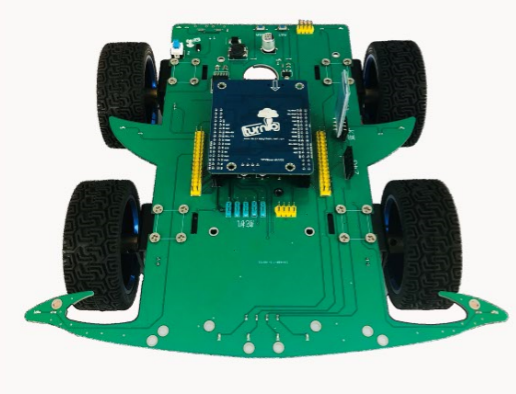
4.单片机-TPYBoard v102
TPYBoard v102 是遵循MIT协议,由TurnipSmart公司制作的一款MicroPython开发板,它基于STM32F405单片机,通过USB接口进行数据传输。该开发板内置4个LED灯、一个加速度传感器,可在3V-10V之间的电压正常工作。让你会Python就能做极客, 用Python控制硬件,支持Python语言的开发板。比树莓派更小巧,更简单,更便宜,比Arduino更强大,更加容易编程。

小车扩展板
以TPYBoard v102开发板为主控板,小车扩展板具有四路PWM调速电机、8个可控LED、1个蜂鸣器、5路舵机接口、1个蓝牙接口、1个PS2无线接口、引出TPYBoard v102开发板全部针脚,可装载循迹模块、超声波模块、机械手臂、红外接收头,兼容入门级电机和专业级电机,两节18650单独供电。
源代码
我们只需要把TPYBoard v102 插小车扩展板上,把蓝牙模块插上,把程序写入就行,下面是main.py源程序
from pyb import Pin
from pyb import UART
led_red=Pin('Y5', Pin.OUT_PP)
led_right=Pin('Y12', Pin.OUT_PP)
led_left=Pin('Y11', Pin.OUT_PP)
led_red.value(1)
led_right.value(0)
led_left.value(0)
#蓝牙模块通信串口
blue=UART(1,9600,timeout=100)
#前左轮
M1_0 = pyb.Timer(8, freq=10000).channel(1, pyb.Timer.PWM, pin=pyb.Pin.board.Y1)
M1_1 = pyb.Timer(8, freq=10000).channel(2, pyb.Timer.PWM, pin=pyb.Pin.board.Y2)
#前右轮
M2_0 = pyb.Timer(4, freq=10000).channel(3, pyb.Timer.PWM, pin=pyb.Pin.board.Y3)
M2_1 = pyb.Timer(4, freq=10000).channel(4, pyb.Timer.PWM, pin=pyb.Pin.board.Y4)
#后左轮
M3_0 = pyb.Timer(1, freq=10000).channel(1, pyb.Timer.PWM, pin=pyb.Pin.board.Y6)
M3_1 = pyb.Timer(1, freq=10000).channel(2, pyb.Timer.PWM, pin=pyb.Pin.board.Y7)
#后右轮
M4_0 = pyb.Timer(2, freq=10000).channel(3, pyb.Timer.PWM, pin=pyb.Pin.board.Y9)
M4_1 = pyb.Timer(12, freq=10000).channel(2, pyb.Timer.PWM, pin=pyb.Pin.board.Y8)
def go(speed):
M1_0.pulse_width(speed*200+10000)
M1_1.pulse_width(0)
M2_0.pulse_width(speed*100+5000)
M2_1.pulse_width(0)
M3_0.pulse_width(speed*220+10000)
M3_1.pulse_width(0)
M4_0.pulse_width(speed*50+5000)
M4_1.pulse_width(0)
led_red.value(0)
def back(speed):
M1_0.pulse_width(0)
M1_1.pulse_width(speed*200+10000)
M2_0.pulse_width(0)
M2_1.pulse_width(speed*100+10000)
M3_0.pulse_width(0)
M3_1.pulse_width(speed*200+10000)
M4_0.pulse_width(0)
M4_1.pulse_width(speed*100+10000)
led_red.value(1)
def stop():
M1_0.pulse_width(0)
M1_1.pulse_width(0)
M2_0.pulse_width(0)
M2_1.pulse_width(0)
M3_0.pulse_width(0)
M3_1.pulse_width(0)
M4_0.pulse_width(0)
M4_1.pulse_width(0)
led_right.value(0)
led_left.value(0)
led_red.value(1)
def left(speed):
M1_0.pulse_width(speed*30+10000)
M1_1.pulse_width(0)
M2_0.pulse_width(speed*100+10000)
M2_1.pulse_width(0)
M3_0.pulse_width(speed*30+10000)
M3_1.pulse_width(0)
M4_0.pulse_width(speed*100+10000)
M4_1.pulse_width(0)
led_right.value(1)
led_left.value(0)
def right(speed):
M1_0.pulse_width(speed*200+20000)
M1_1.pulse_width(0)
M2_0.pulse_width(speed*200+3000)
M2_1.pulse_width(0)
M3_0.pulse_width(speed*100+20000)
M3_1.pulse_width(0)
M4_0.pulse_width(speed*100+3000)
M4_1.pulse_width(0)
led_right.value(0)
led_left.value(1)
if __name__ =='__main__':
stop()
while True:
if blue.any()>0:
data=blue.read().decode()
print(data)
if data.find('0')>-1:
#stop
stop()
print('stop')
if data.find('1')>-1:
pyb.LED(2).on()
pyb.LED(3).off()
pyb.LED(4).off()
#-------------
go(5)
print('go')
if data.find('2')>-1:
pyb.LED(2).off()
pyb.LED(3).on()
pyb.LED(4).off()
#-------------
back(5)
if data.find('3')>-1:
pyb.LED(2).off()
pyb.LED(3).off()
pyb.LED(4).on()
left(5)
if data.find('4')>-1:
pyb.LED(2).off()
pyb.LED(3).off()
pyb.LED(4).on()
right(5)